Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, there’s a lot of misinformation and stigma surrounding the condition. In this blog post, we will explore what genital herpes is, how it transmits, the signs and symptoms in both men and women, other types of herpes, and ways to protect yourself and manage the condition.
What is Genital Herpes?
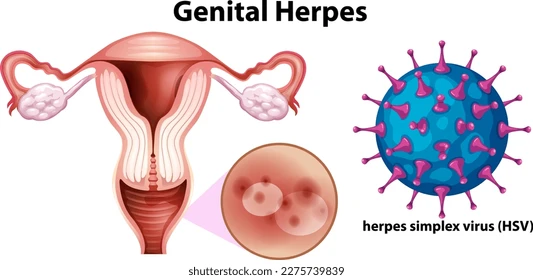
Genital herpes is an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two types of HSV:
- HSV-1: Typically associated with oral herpes (cold sores around the mouth), but it can also cause genital herpes through oral-genital contact.
- HSV-2: The primary cause of genital herpes, which leads to outbreaks of sores or blisters in the genital and anal areas.
Once infected, the virus stays in the body for life, residing in nerve cells, and can become active again, leading to outbreaks. However, not all infected individuals experience symptoms, and some may never have visible outbreaks, making it possible to transmit the virus without knowing.
How is Genital Herpes Transmitted?
Genital herpes is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected area. It can spread during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and sometimes even through close contact with an infected person’s skin. HSV can be passed on even when there are no visible sores or symptoms, a phenomenon known as asymptomatic shedding.
Common ways genital herpes is transmitted include:
- Vaginal sex: Contact with the infected partner’s genital area.
- Oral sex: If a person with oral herpes (caused by HSV-1) performs oral sex, they can transmit the virus to the genital area.
- Anal sex: Contact with sores or infected skin around the anus.
- Touching sores: If someone touches an active herpes sore and then touches their own or someone else’s genital area, transmission can occur.
Herpes is not spread through casual contact, such as sharing towels, toilet seats, or bathing together.
Signs and Symptoms of Genital Herpes
The symptoms of genital herpes can vary widely between individuals. Some people may not show any signs of infection, while others may experience recurrent outbreaks of painful sores.
Early Signs Before Intercourse in Men and Women
In both men and women, early signs of an impending outbreak (sometimes referred to as prodromal symptoms) may appear before visible sores develop. These can include:
- Tingling or itching: A tingling or itching sensation in the genital or anal area.
- Burning sensation: Some people may feel a burning sensation when urinating.
- Pain: Mild to moderate pain in the lower back, buttocks, or thighs.
Recognizing these early signs is important, as it can help individuals avoid sexual activity during this period, reducing the risk of transmission.
Symptoms in Men:
- Sores or blisters: Painful blisters or ulcers may appear on the penis, scrotum, anus, or thighs.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Some men may experience swollen lymph nodes in the groin area.
- Painful urination: If sores are present near the urethra, urination can be painful.
Symptoms in Women:
- Sores or blisters: Painful blisters or ulcers may appear on the vulva, vagina, cervix, anus, or inner thighs.
- Vaginal discharge: Some women may experience an abnormal discharge.
- Painful urination: If sores are located near the urethra, urination can be painful or difficult.
Both men and women may also experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, body aches, or swollen glands during their first outbreak.
Other Types of Herpes
While genital herpes is caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2, there are other forms of herpes infections, including:
- Oral Herpes (Cold Sores): Caused by HSV-1, this infection typically appears as sores around the mouth and lips. Oral herpes can be transmitted to the genital area through oral sex.
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles): Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox, shingles results in painful blisters that typically appear on one side of the body.
- Ocular Herpes: A rare form of herpes that affects the eyes, leading to pain, swelling, and potential vision loss.
How to Protect Yourself from Genital Herpes
While genital herpes cannot be completely cured, there are ways to protect yourself and reduce the risk of transmission:
- Use Condoms: Condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting genital herpes, but they do not completely eliminate the risk because herpes can be present on areas not covered by a condom.
- Avoid Sexual Contact During Outbreaks: If you or your partner have an active herpes outbreak (sores or symptoms), avoid all forms of sexual contact until the sores have fully healed.
- Talk Openly with Your Partner: It’s important to have an open conversation with your partner about STIs, including herpes, and get tested regularly if you are sexually active.
- Antiviral Medications: Individuals with genital herpes can take daily antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir, to reduce the frequency of outbreaks and lower the risk of transmitting the virus to partners.
- Avoid Oral Sex During Cold Sore Outbreaks: If you or your partner has oral herpes (cold sores), avoid oral-genital contact during an outbreak to prevent spreading HSV-1 to the genital area.
Treatment and Managing Genital Herpes
While there is no cure for genital herpes, there are several treatments available to manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks:
- Antiviral Medications: These can shorten the duration of outbreaks and reduce the severity of symptoms. Medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can also be taken daily (suppressive therapy) to prevent frequent outbreaks.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain during outbreaks.
- Topical Creams: Some topical antiviral creams can help reduce the severity of cold sores or genital herpes blisters, but their effectiveness is limited.
It’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, as factors like stress, illness, or fatigue can trigger outbreaks. Regular medical consultations and antiviral medications can help manage the condition effectively.
Conclusion
Genital herpes is a lifelong condition, but with the right knowledge, precautions, and treatment, it can be managed. Understanding how the virus transmits, recognizing early symptoms, and taking steps to protect yourself and your partner can reduce the impact of the virus on your life. If you suspect you have genital herpes or have been exposed, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss testing, treatment, and strategies for managing the condition.