The Anti-Mullerian Hormone Test: A Window into Fertility Health
When it comes to fertility, knowledge is power. The Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) test has revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine by providing valuable insights into a person’s ovarian reserve and potential fertility. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of the AMH test. We will explore what AMH is, its role in fertility, why the test is conducted, how it is performed, and what the results can indicate. Understanding this crucial test empowers individuals and couples to make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
What is Anti-Mullerian Hormone?
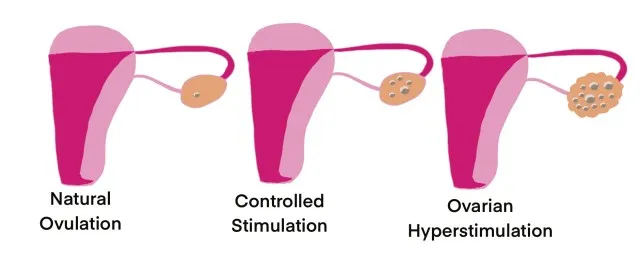
Anti-Mullerian Hormone is a protein hormone produced by the cells in the developing follicles of the ovaries. It plays a crucial role in regulating the growth and development of ovarian follicles, which contain immature eggs. As follicles mature, they produce increasing amounts of AMH. The hormone levels in the blood are an indicator of the ovarian reserve, representing the number of eggs remaining in the ovaries.
Why is the AMH Test Conducted?
The AMH test is commonly performed in reproductive medicine to assess a person’s ovarian reserve and potential fertility. It is especially useful for individuals undergoing fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or considering egg freezing. The test helps determine the response to ovarian stimulation, guide treatment protocols, and predict the likelihood of success. Additionally, the AMH test can assist in diagnosing certain reproductive conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), premature ovarian insufficiency, or primary ovarian insufficiency.
The AMH Test Procedure: The AMH test is a simple blood test that can be performed at any point in the menstrual cycle. A small blood sample is typically collected from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually available within a few days.
Interpreting the Results: The AMH test provides an indication of the ovarian reserve. Higher levels of AMH generally suggest a larger number of remaining follicles and potentially better fertility potential. Lower AMH levels may indicate a reduced ovarian reserve, suggesting a decreased number of eggs and potentially reduced fertility. However, it’s important to note that AMH levels alone cannot predict the chances of achieving pregnancy or the quality of the remaining eggs.
Considerations and Limitations
While the AMH test is a valuable tool in assessing ovarian reserve, it is just one piece of the fertility puzzle. Factors such as age, overall health, and other fertility-related tests should be considered in conjunction with AMH results. Additionally, it’s essential to consult with a reproductive specialist or healthcare provider to interpret the test results accurately and discuss the implications for fertility treatment or family planning.
The Anti-Mullerian Hormone test offers valuable insights into a person’s ovarian reserve and potential fertility. By understanding the role of AMH, why the test is conducted, and how to interpret the results, individuals and couples can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and seek appropriate medical guidance when needed.
If you want to read more about IVF, make sure to check out the top clinic in Cyprus’ website, Crown IVF.
Make sure to check out our most recent blog post about sperm donation.